KuberLogic Introduction
KuberLogic is a SaaS enabler for Software vendors that have a single-tenant application and helps easily turn this existing application into a Software as a Service offering. KuberLogic allows software vendors to start their SaaS journey here and now with minimal application modidication.
How KuberLogic works
KuberLogic is based on Kubernetes, which provides freedom from vendor lock-in (as it can be deployed anywhere), as well as high solution flexibility and resource utilization efficiency. Kuberlogic works with applications packaged in the form of a docker-compose file, which is widely used and has a fairly low entry threshold, a huge number of projects are already packaged in a docker-compose file, which ensures a quick start for them. After uploading the application to KuberLogic, KuberLogic provides the capability for orchestration of tenants (provision/list/delete/edit) in Kubernetes using the namespace per tenant model, which represents a good blend of isolation and cost efficiency.
In this conception, each tenant (application instance) is deployed into the same cluster but separated from one another using namespaces and a series of native and add-on Kubernetes constructs. This is what’s commonly referred to as a “silo” model where tenant resources are not shared by tenants, providing, among other things, protection from noisy neighbors for Tenants. Also, this model is commonly referred to as “multi-instance”.
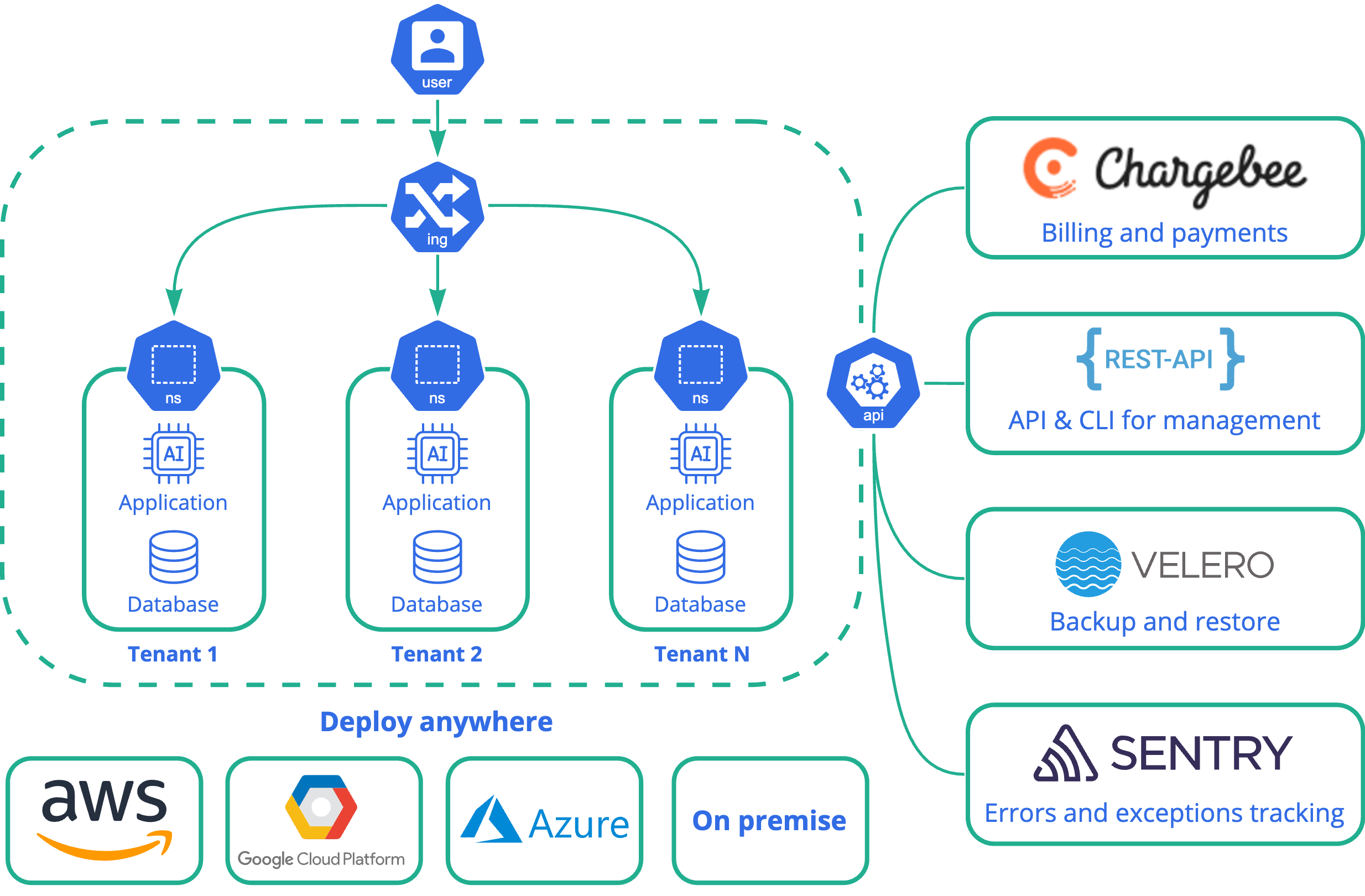
Multi-instance architecture benefits:
- Stability— Instead of a single point of failure (the single application instance), each customer can exist in their own instance. If one instance fails, the others will remain unaffected.
- Scalability — With a multi-instance architecture, scaling up is a simple matter of adding more resources. However, with a multi-tenant architecture, you could reach a point where you need to come up with a clustered application architecture whose deployment is usually far from trivial.
- Security — When you are using a single database, all your data lives together. This becomes a major problem in the event of a security breach because all customers’ data can become vulnerable when a single account is compromised. With a multi-instance architecture, only a single customer’s data can be at risk.